Introduction
Business Events provides a mechanism which lets external systems receive notifications in near real time from Dynamics 365 Finance and Supply Chain. The external systems can then perform additional business actions in response to the business events. A business action that a user performs can be either a workflow action or a non-workflow action. Approval of a purchase requisition is an example of a workflow action, whereas confirmation of a purchase order is an example of a non-workflow action.
Before moving forward, we should understand that business events must not be considered a mechanism for exporting expensive payloads of data. By definition, business events are supposed to be lightweight and nimble. They aren’t intended to carry large payloads to fulfill data export scenarios.
Some use cases for business events:
Procurement: It improves the communication between the back-office team and production team by sending an event when a production order is created. The production floor team will get notified by third party applications so they can speed up the process of production.
Sales orders: This allows businesses with third-party warehouses to send the picking information to the system. Confirmation or picking of a sales order triggers a business event which external systems (third-party warehouses) can use to analyse and determine the picking priority and utilisation.
Reporting: Managers can be informed about newly created financial reports. This allows prompt follow-up and faster engagement.
Business Event Catalog:
This is the main form which lists down all the available business events in the instance that you are using and can be accessed from System administration > Set up > Business events. Events are categorised by module or originate from a workflow system and are then assigned to the workflow category. The catalog also shows the list of data fields that will be sent out in the event.
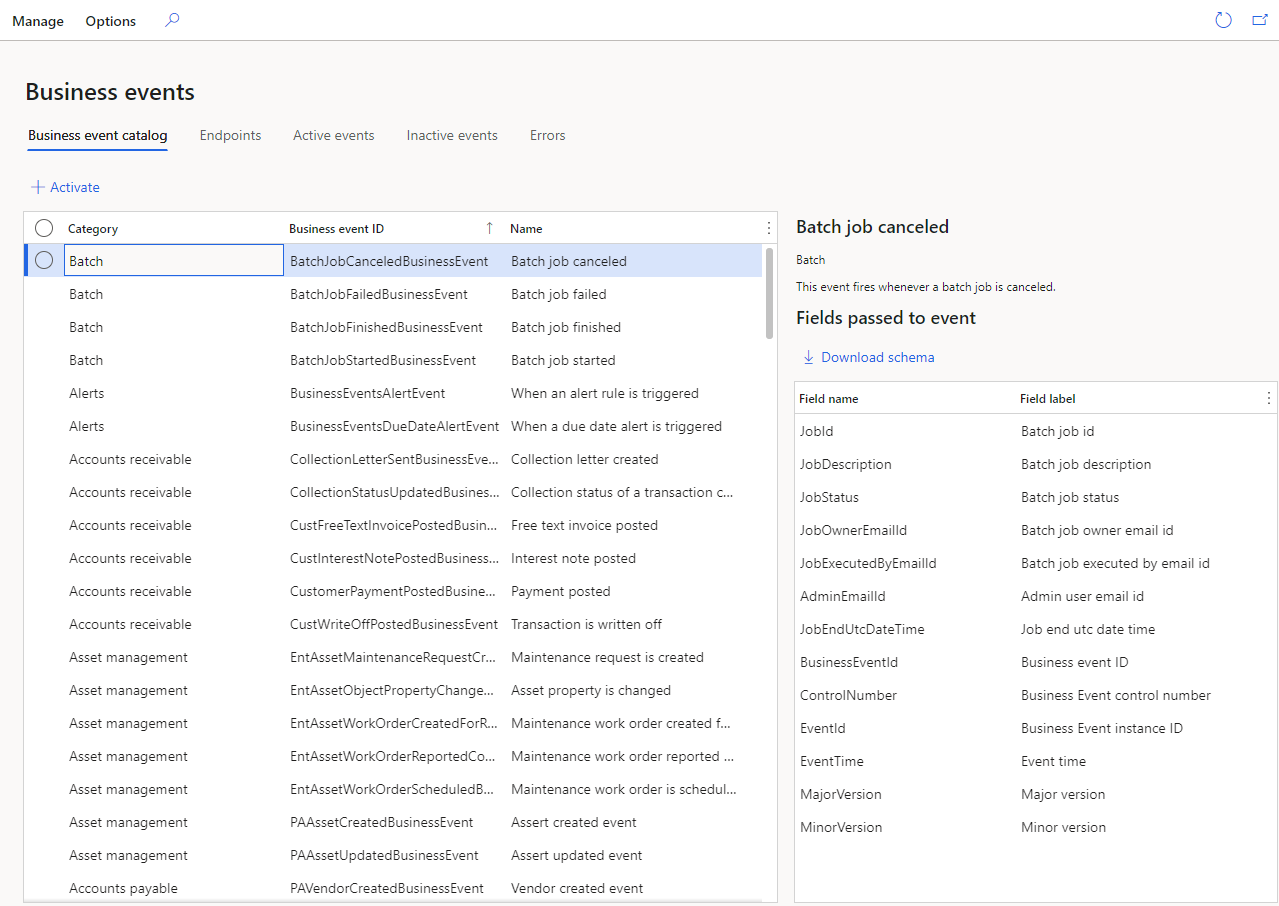
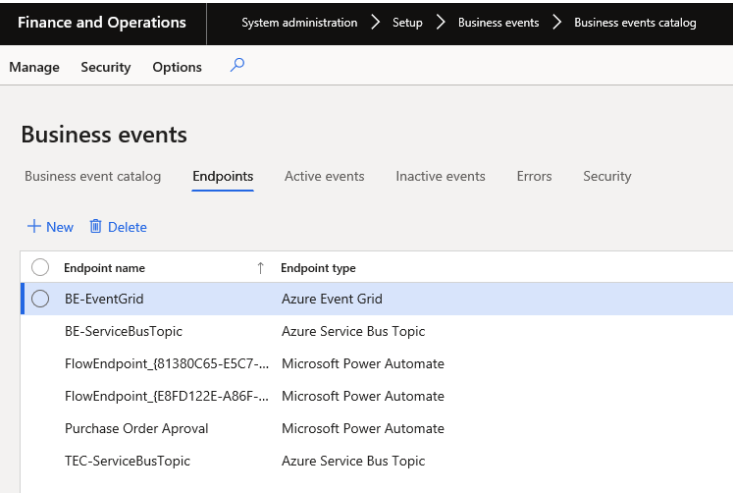
Supported Endpoints:
Endpoints such as Microsoft Flow and Azure Service Bus can subscribe to these business events and get the payload information to trigger additional automated actions, both within Dynamics 365 Finance and Supply Chain as well as within external systems. The following types of endpoints are currently supported, and endpoints can be created for these messaging and event brokers out of the box.
- Azure Service Bus Queue.
- Azure Service Bus Topic.
- Azure Event Grid.
- Azure Event Hub.
- HTTPS.
- Microsoft Power Automate.
Azure based end points must be in the customer’s Azure subscription (ex: Azure Service Bus Queue/Topic, Event grid).
When a business event occurs and there is an active endpoint, the payload gets sent out. In case the endpoints are down, it will be captured in the error log.
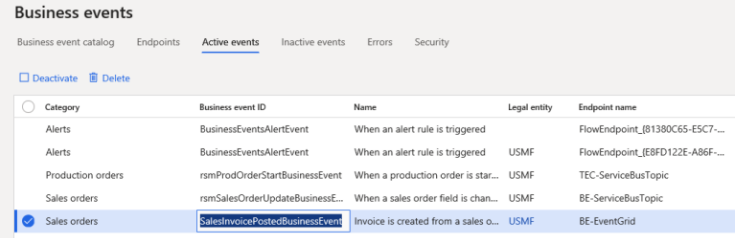
Activating business events:
Business events are not active by default. From the catalog, you can activate any events that are required, and can activate either in all legal entities or in specific legal entities. At the time of activation, you need to mention a valid endpoint. When business events occur as business processes are run, the system will do outbound processing only for business events that have been activated.
When business requirements change, some business events may no longer be required. You can de-activate them instead of deleting and preserve the history of errors.
Developing new business events
Before implementing a new business event, you need to understand the intent behind capturing a business event. If the intent is to capture an event and take a business action outside Dynamics 365 in response to a business event, that is a good use case. If the intent is to transfer data to a recipient like data export, that is not a good use case, but instead is a misuse of the business event framework.
Also, the fidelity of business events is significant. For example, no false business events should be sent to the recipient. If a purchase order confirmation business event is sent out, the recipient expects and must trust that the purchase order was really confirmed.
Business events should be specific and must be targeted to specific use cases. In other words, they should not be generic, so the consumer must evaluate what a business event is for by trying to understand the payload.





