Analytical Accounting is a tool within Microsoft Dynamics GP that allows users to further analyse their financial data at a granular level, in more detail than the general ledger and chart of accounts.
During data entry, transactions can be assigned an analytical accounting code to further analyse the value into additional dimensions.
Examples of travel expenses analysed by region:
Let us take a travel expense as an example. In the chart of accounts we have one general ledger account assigned to Travel Expenses. We also want to be able to analyse the total travel expenditure by state or region. Analytical Accounting codes are set up for each of the regions we want to analyse. When an accounts payable or another expense transaction type is keyed into Dynamics GP, the user allocates specific amounts to different regions set up as analytical accounting codes. At the general ledger level, the total is all being allocated to the same account.
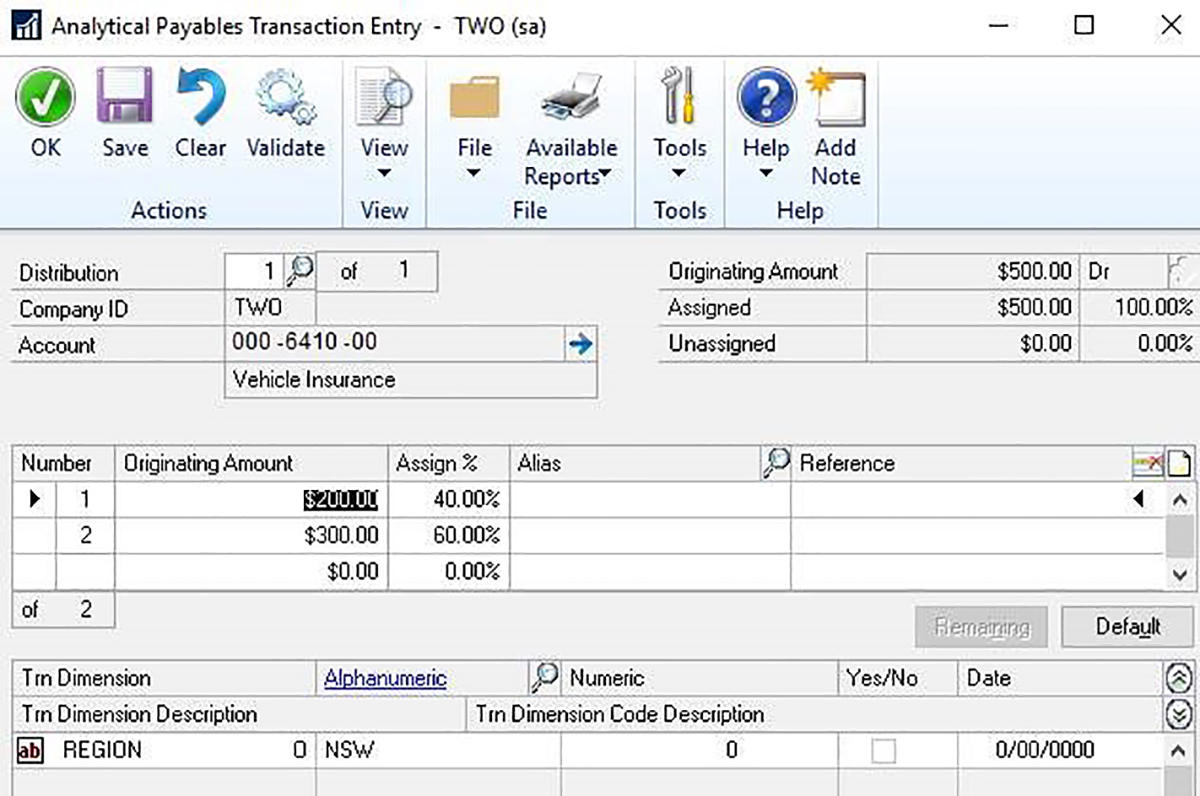
In this payables transaction, although the total expense of $500 is allocated to one General Ledger account 000-6410-00, the $500 can be allocated or split as follows: $200 to Analysis Codes NSW and $300 to Analysis Codes VIC.
The use of analytical accounting codes during data entry offers greater reporting flexibility without the need to create multiple general ledger accounts and added complexity to the chart of accounts.
The benefits of Analytical Accounting:
- Once an AA code is set up, it is available within all areas of Dynamics GP.
- Dimensions can be restricted so they are only used in specific modules, e.g. allowed for Account Payables transactions but not allowed for Account Receivables data entry.
- A General Ledger account can have multiple dimensions assigned to it, one dimension, or none. Once the rule is set up, it can be enforced that during data entry an AA code is required to minimise data entry errors.
- Analytical Accounting codes can be activated or deactivated as the business requirements change.
- The AA module includes budgeting functionality where teams can enter budgets for an analytical accounting code and then compare to actuals.
- Using the AA functionality users can store statistical information such as units of labour in hours, days, etc. It is not restricted to financial values.
What are some common use cases for Analytical Accounting?
Analytical Accounting is very versatile and can be adapted to suit different transactional analysis requirements. The following are examples of some use cases:
- Management of grants in not-for-profit organisations.
- Job income and expenditure analysis in project-based organisations.
- Detailed analysis of IT expenditure.
- Employee benefits tracking for FBT reporting.
- Travel expenditure by employee.
Are you considering adding Analytical Accounting to your Dynamics GP deployment?
Learn how to analyse Dynamics GP Analytical Accounting data with Power BI in this on-demand webinar.






